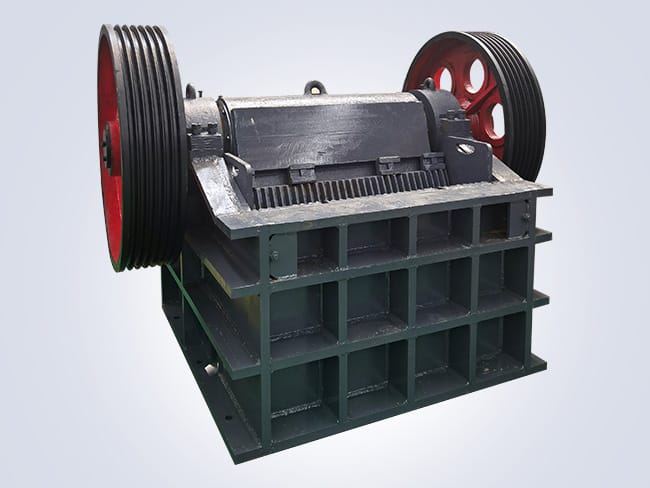
A jaw crusher is a primary crushing equipment widely used in industries such as mining, construction, and chemicals. Its working principle mainly involves the use of two jaw plates—a fixed jaw plate. And a movable swing jaw plate—that crush materials through compression between them. Due to its simple structure, easy operation, convenient maintenance. And high crushing ratio, the jaw crusher holds an important position in mineral processing.
How a Jaw Crusher Crushes Materials
The core components of a jaw crusher are the two jaw plates, with one fixed to the crusher’s frame. Known as the fixed jaw plate, and the other connected to an eccentric shaft via a connecting rod. Known as the swing jaw plate. When the eccentric shaft rotates, the swing jaw plate moves back and forth. Thus achieving the compression and crushing of materials. Materials enter the crushing chamber from the feed inlet at the top. And are gradually crushed under the action of the swing jaw plate, eventually being discharged from the outlet at the bottom.
The structure of a jaw crusher is relatively simple, consisting mainly of the frame, movable jaw, fixed jaw, eccentric shaft, connecting rod mechanism, spring device, and driving device. The movable jaw is connected to the eccentric shaft via the connecting rod, and the eccentric shaft is driven by an electric motor. The reciprocating motion of the movable jaw is generated by the eccentric shaft, ensuring that materials are evenly subjected to force during the crushing process.